
115kV SF6 Circuit Breaker. Photo: Wikimedia.
Sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) – an excellent insulating and arc quenching gas.
Substantial properties of SF6 at a glance
SF6 gas is a widely used insulating and arc-quenching medium in power distribution systems, known for its excellent electrical properties and ability to extinguish electrical arcs.
- Colorless and odorless
- 5 times heavier than air
- Temperature-resistant up to 500 °C
- Chemically stable
- Non-toxic
- Excellent dielectric properties
- Non-inflammable
- Outstanding arc quenching properties
Advantages of SF6
SF6 has a number of advantages for use as an insulator. The dielectric strength of SF6 increases with pressure so smaller breakers can be used at higher voltages.
These circuit breakers have a smaller footprint, so they use less real estate which can be very expensive. Gas insulated breakers are very reliable and require less maintenance than air blast or oil breakers and can operate at higher voltages effectively.
SF6 in cold climates
Nitrogen and freon-14 are added to keep SF6 gasified at lower temperatures. SF6 has a tendency to liquefy and pool at colder temperatures. This reduces the internal pressure, which reduces the dielectric strength.

SF6 Circuit Breakers in Substation. Photo: Wikimedia.
Dead Tanks vs. Live Tanks
Dead tank breakers have grounded tanks. Live tank breakers use the insulating column to house the mechanism and contact assemblies, so they are energized at system voltage (live).
Moisture in SF6 gas
SF6 is known for its excellent arc quenching properties, which make it effective in extinguishing electrical arcs. However, moisture can degrade the insulation properties of SF6, reducing its dielectric strength and increasing the risk of electrical breakdown or flashover.
New equipment containing SF6 gas is tested for moisture in accordance with ASTM D2029. The acceptable limit can be found in NETA ATS Table 100.13, which specifies -62°C or 8.3 ppmv max.
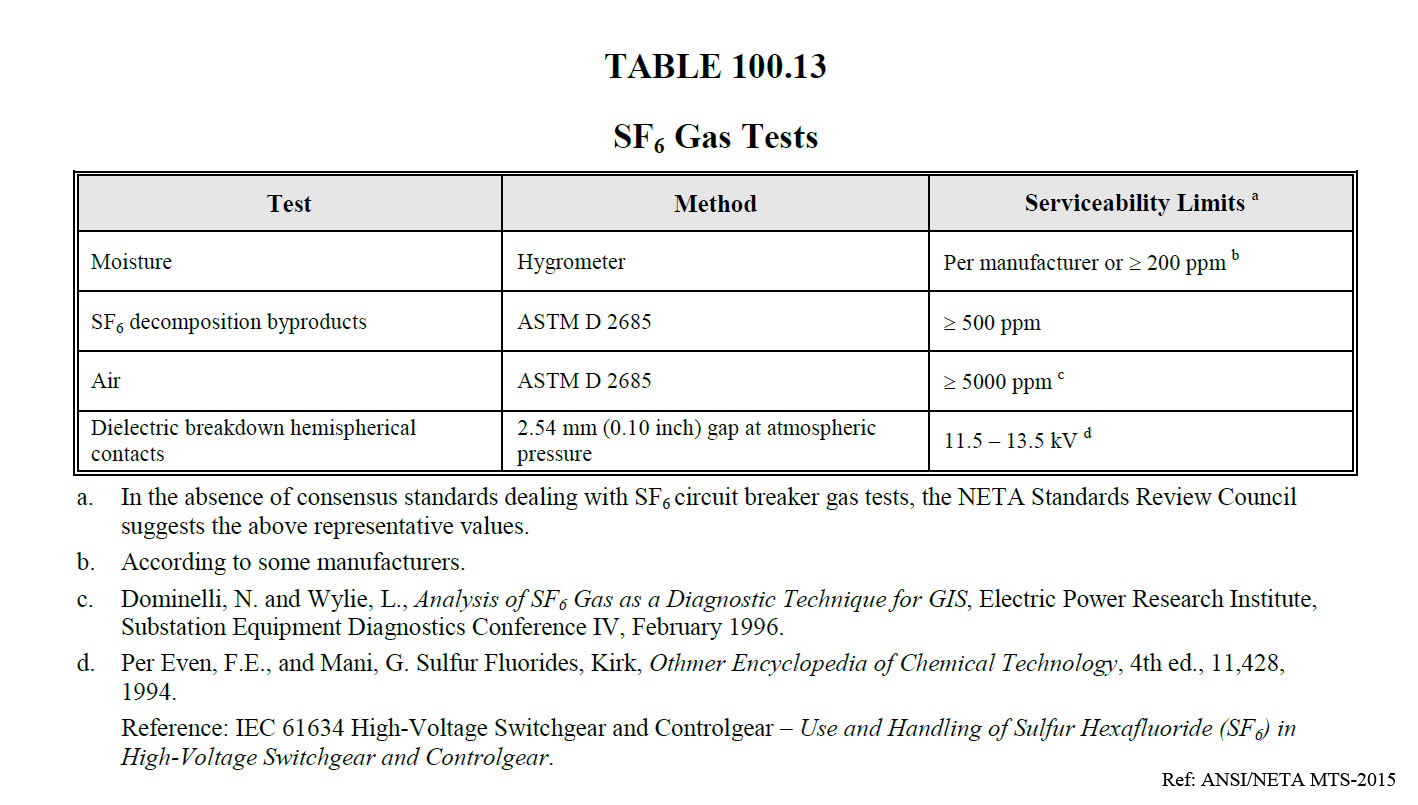
The gas limits for in-service SF6 are found in ANSI/NETA MTS Table 100.13. This table is derived from IEC 60480 Guidelines for the checking and treatment of sulfur hexafluoride taken from electrical equipment and specification for re-use, Table 2.
ANSI/NETA MTS-2023 specifies several limits for water content in pure SF6 gas depending on the type of vessel and switching application. Prior versions of this standard allowed a limit of 200 ppm moisture of in-service SF6 gas.
Parts per million by volume (PPMV)
PPMV stands for parts per million by volume, and it is a unit of measurement used to express the concentration of a particular substance in a gas mixture. When referring to SF6 moisture content, ppmv represents the number of moisture molecules present per one million molecules of SF6 gas. It is used to quantify the level of moisture contamination in SF6 gas, which is important to monitor and control to ensure the proper functioning and insulation properties of electrical equipment.
Hazardous Byproducts in SF6 gas
As SF6 decomposes during arcing metal fluorides are created, which are corrosive. When servicing SF6 breakers that have been faulted, full body protection and oxygenfed respirators may be needed to prevent the fluorides from contacting the skin or being inhaled. Any moisture on or in the body will create hydrofluoric acid.
4 Risk Categories of SF6 gas Contamination
Contamination in SF6 gas can occur due to various factors, including arcing, handling, and storage. These risk categories help in determining the appropriate maintenance and testing procedures for SF6 gas-insulated equipment, as higher levels of contamination can increase the risk of equipment failure and reduce its reliability.
- New gas – in cylinders from the gas manufacturer.
- Non-arced – has been used or handled, but contains no arcing byproducts
- Normally arced – corrosive byproducts less than 200 ppm
- Heavily arced – contains arcing byproducts greater than one percent by volume.
SF6 Gas Tests Limits
Maintaining the appropriate levels of SF6 gas purity and moisture content is critical to ensure the insulation and arc extinguishing properties of the gas are not compromised. This helps prevent electrical faults, equipment failures, and potential safety hazards.
Adhering to the specified testing limits helps ensure that electrical equipment utilizing SF6 gas operates within the manufacturer’s recommended specifications and industry standards. The testing limits provided in NETA Table 100.13 outline acceptable levels of SF6 gas purity and moisture content.
NETA ATS-2020 Table 100.13 SF6 Gas Test Limits
NETA MTS-2023 Table 100.13 SF6 Gas Test Limits
NETA MTS-2015 Table 100.13 SF6 Gas Tests


